MongoDB Getting Started
MongoDB is a scalable, high-performance, open source NoSQL database written in C++.MongoDB, Inc. is the company behind the database for GIANT ideas, offering the best of traditional databases as well as the flexibility, scale and performance today’s applications require. We build MongoDB and the drivers, offer software and services, run MongoDB University (which has trained over 350,000 engineers in MongoDB), and sponsor the MongoDB community.
If you have installed Websoft9 MongoDB, the following steps is for your quick start
Preparation
- Get the Internet IP of your Server on Cloud
- Check your Inbound of Security Group Rule of Cloud Console to ensure the TCP:27017,9091 is allowed
- Complete Five steps for Domain if you want to use Domain for MongoDB
- Get default username and password of MongoDB
MongoDB Initialization
Steps for you
You should verify the MongoDB when completed deployment:
Check MongoDB
- Use the SSH to connect Server, and run the command below to view the installation information and running status
cd /data/apps/mongodb && sudo docker compose ls - You can ge the message from SSH " STATUS: running(1) " when MongoDB is running
Connect MongoDB
-
Use the SSH to connect Server, and run MongoDB shell (Don't have password?)
$ docker exec -it mongodb mongo admin -u root -p YOURPASSWORD
MongoDB shell version v5.0.10
connecting to: mongodb://127.0.0.1:27017/?compressors=disabled&gssapiServiceName=mongodb
{"t":{"$date":"2022-08-10T03:05:34.194Z"},"s":"I", "c":"NETWORK", "id":5693100, "ctx":"js","msg":"Asio socket.set_option failed with std::system_error","attr":{"note":"connect (sync) TCP fast open","option":{"level":6,"name":30,"data":"01 00 00 00"},"error":{"what":"set_option: Protocol not available","message":"Protocol not available","category":"asio.system","value":92}}}
Implicit session: session { "id" : UUID("030a4e0b-54cf-4f93-aa90-792b10c478f7") }
MongoDB server version: 5.0.10
================
Warning: the "mongo" shell has been superseded by "mongosh",
which delivers improved usability and compatibility.The "mongo" shell has been deprecated and will be removed in
an upcoming release.
For installation instructions, see
https://docs.mongodb.com/mongodb-shell/install/
================
> -
List all databases and users
# list all databases
show dbs
# use admin, and list all users
use admin
show users
Having trouble?
Below is for you to solve problem, and you can contact Websoft9 Support or refer to Troubleshoot + FAQ to get more.
Does MongoDB enable account authentication by default?
YES, Mongodb authentication is enabled by default.
MongoDB QuickStart
To learn more about the use of mongodb, refer to the official document MongoDB Administration
MongoDB Setup
Enable MongoDB remote connection
-
Use SSH to connect MongoDB server and modify the MongoDB configuration file
#1 set authorization **disabled** to **enabled**
security:
authorization: enabled
#2 set bindIP to 0.0.0.0
net:
port: 27017
bindIp: 0.0.0.00.0.0.0 means any Internet IP can connect your MongoDB
-
Restart MongoDB service
sudo docker restart mongodb -
Go to the Cloud Console and enable the TCP:27017 port of Security Group
Close MongoDB access authentication
Mongodb authentication is enabled by default, and can be closed according to the following process:
-
Edit MongoDB configuration file, comment out the environment variable user and password.
services:
mongo:
image: mongo:${APP_VERSION}
restart: always
container_name: ${APP_NAME}
ports:
- ${APP_MONGO_PORT}:27017
#environment:
# MONGO_INITDB_ROOT_USERNAME: ${APP_USER}
# MONGO_INITDB_ROOT_PASSWORD: ${APP_PASSWORD} -
Recreate MongoDB container
cd /data/apps/mongodb
sudo docker compose up -d
MongoDB web GUI
Now, we will introduce how to use MongoDB compass
Preparation
- Open the access authentication of MongoDB
- Check your Inbound of Security Group Rule of Cloud Console to ensure the TCP:9091 is allowed
When completed the preparation, you can use the GUI now
- Open Chrome or Firefox on your local PC to visit URL http://Internet IP:9091, follow the prompts to enter the user name and password(Don't have password?)
- Click the MongoDB compass icon on the web desktop to enter MongoDB compass

- Fill in the correct items and connect MongoDB
# example connect string
mongodb://root:1cTFecwTEs@mongodb:27017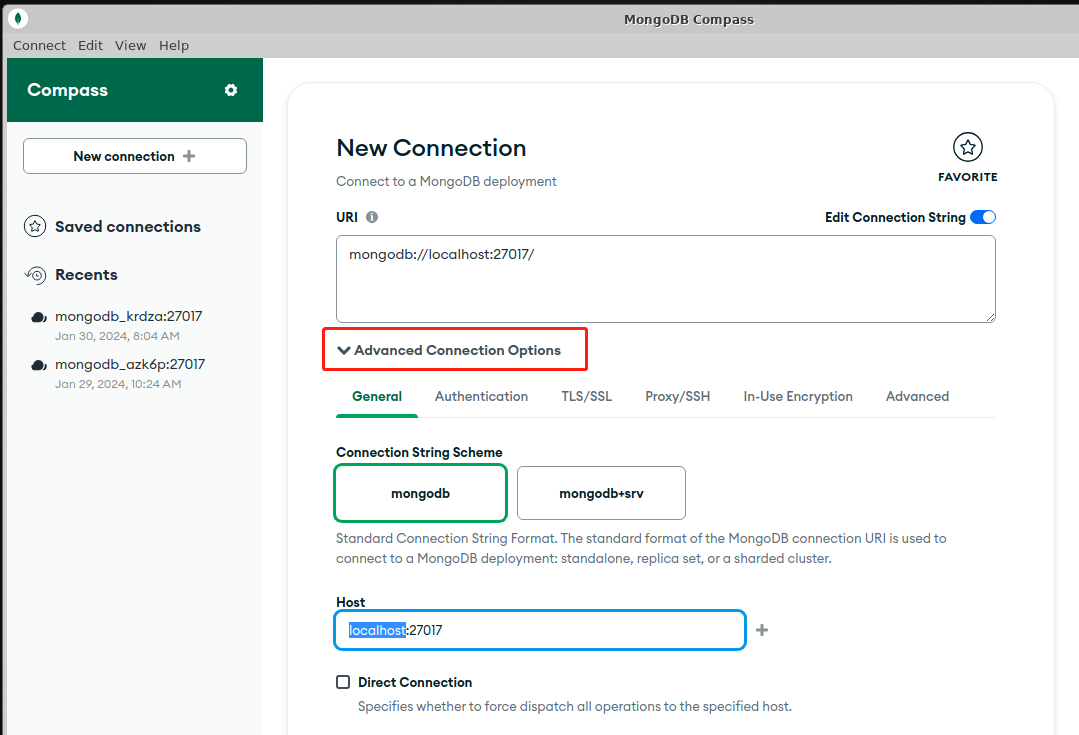
- Go go MongoDB Compass console when connect successfully
Planning data model
MongoDB as a kind of database, it is also similar to the traditional RDBMS, that is, planning the data model and establishing the database paradigm.
Only in this way can the performance of the database be better developed.
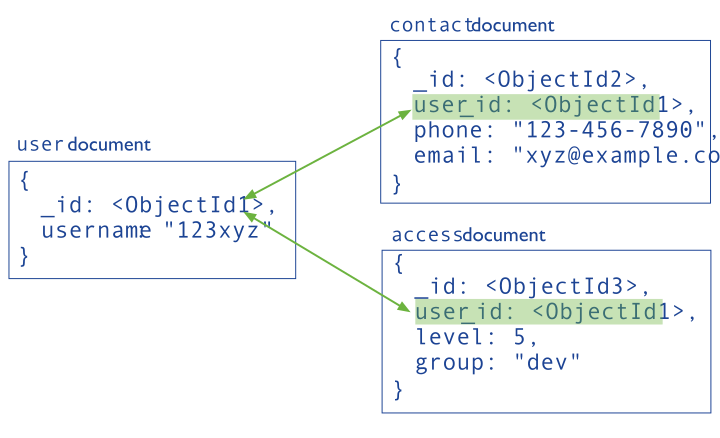
The main design points of data planning include:
- Use data paradigm
- Using embedded document anti paradigm
- Use fixed sets
- Consider document enlargement
- Planning indexing, sharding, and replication
- Planning data lifecycle
Useful MongoDB Command
show all database, create database, insert data
> show dbs
admin 0.000GB
config 0.000GB
local 0.000GB
-------------------------
#2 create database test, if there have test, it's means switch to test, example
> use test
switched to db test
# show the current database
> db
test
# show the current database users
> show users
-------------------------
#3 Insert data into the database test, example
> db.test.insert({"name":"company"})
WriteResult({ "nInserted" : 1 })
-------------------------
Delete the database
> show dbs
admin 0.000GB
config 0.000GB
local 0.000GB
test 0.000GB
websoft9 0.000GB
> use test
switched to db test
> use test
> db.dropDatabase()
{ "dropped" : "test", "ok" : 1 }
> show dbs
admin 0.000GB
config 0.000GB
local 0.000GB
websoft9 0.000GB
Create administrator user
> mongo
> use admin
switched to db admin
> db.createUser( { user: "webs_admin", pwd: "websoft9", roles: ["userAdminAnyDatabase"] } )
Successfully added user: { "user" : "webs_admin", "roles" : [ "userAdminAnyDatabase" ] }
# Show account number
> show users
{
"_id" : "admin.webs_admin",
"user" : "webs_admin",
"db" : "admin",
"roles" : [
{
"role" : "userAdminAnyDatabase",
"db" : "admin"
}
],
"mechanisms" : [
"SCRAM-SHA-1",
"SCRAM-SHA-256"
]
}
Password management
Modify password
You can modify the password of root user which added on your MongoDB by the following command
$ docker exec -it mongodb mongo admin -u root -p YOURPASSWORD
MongoDB shell version v4.0.18
connecting to: mongodb://127.0.0.1:27017/?gssapiServiceName=mongodb
> db = db.getSiblingDB('admin')
admin
> db.changeUserPassword("root", "NEWPASSWORD")
> exit
Reset password
Reset password is the process of resetting a new password through special solutions in case the password has been forgotten.
-
Edit MongoDB configuration file, comment out the environment variable user and password.
services:
mongo:
image: mongo:${APP_VERSION}
restart: always
container_name: ${APP_NAME}
ports:
- ${APP_MONGO_PORT}:27017
#environment:
# MONGO_INITDB_ROOT_USERNAME: ${APP_USER}
# MONGO_INITDB_ROOT_PASSWORD: ${APP_PASSWORD} -
Recreate MongoDB container
cd /data/apps/mongodb
sudo docker compose up -d -
Run the MongoDB command to set new password
$ docker exec -it mongodb nongo
> db = db.getSiblingDB('admin')
admin
> db.changeUserPassword("root", "NEWPASSWORD") -
Edit MongoDB configuration file, make the environment variable user and password effective
services:
mongo:
image: mongo:${APP_VERSION}
restart: always
container_name: ${APP_NAME}
ports:
- ${APP_MONGO_PORT}:27017
environment:
MONGO_INITDB_ROOT_USERNAME: ${APP_USER}
MONGO_INITDB_ROOT_PASSWORD: ${APP_PASSWORD} -
Recreate MongoDB container, and the new password will take effect immediately
cd /data/apps/mongodb
sudo docker compose up -d
Reference sheet
The below items and General parameter sheet is maybe useful for you manage MongoDB
Run docker ps, view all containers when MongoDB is running:
CONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS NAMES
80130e1088b2 websoft9dev/mongocompass:v1.31 "/dockerstartup/kasm…" 2 minutes ago Up About a minute 4901/tcp, 5901/tcp, 0.0.0.0:9091->6901/tcp, :::9091->6901/tcp mongocompass
c17d12157c01 mongo:latest "docker-entrypoint.s…" 4 minutes ago Up 4 minutes 0.0.0.0:27017->27017/tcp, :::27017->27017/tcp mongodb
Path
MongoDB install directory: /data/apps/mongodb
MongoDB data directory: /data/apps/mongodb/data/mongo_data
MongoDB configuration file: /data/apps/mongodb/src/mongod.conf
MongoDB compose file: /data/apps/mongodb/docker-compose.yml
Port
| Port | Use | Necessity |
|---|---|---|
| 9091 | HTTP access MongoDB Compass | Optional |
| 27017 | MongoDB Server | Optional |
Version
docker exec -i mongodb mongo --version
Service
sudo docker start | stop | restart mongodb
sudo docker start | stop | restart mongocompass
CLI
Server
The service end of MongoDB is called mongod. After entering the container, you can accept a series of parameters through the mongod command or through the configuration file:
CLI Arguments
-v [ --verbose ] [=arg(=v)] be more verbose (include multiple times
for more verbosity e.g. -vvvvv)
--quiet quieter output
--port arg specify port number - 27017 by default
--logpath arg log file to send write to instead of
stdout - has to be a file, not
directory
--syslog log to system's syslog facility instead
of file or stdout
--syslogFacility arg syslog facility used for mongodb syslog
message
--logappend append to logpath instead of
over-writing
--logRotate arg set the log rotation behavior
(rename|reopen)
--timeStampFormat arg Desired format for timestamps in log
messages. One of ctime, iso8601-utc or
iso8601-local
--setParameter arg Set a configurable parameter
-h [ --help ] show this usage information
--version show version information
-f [ --config ] arg configuration file specifying
additional options
--bind_ip arg comma separated list of ip addresses to
listen on - localhost by default
--bind_ip_all bind to all ip addresses
--ipv6 enable IPv6 support (disabled by
default)
--listenBacklog arg (=128) set socket listen backlog size
--maxConns arg max number of simultaneous connections
- 1000000 by default
--pidfilepath arg full path to pidfile (if not set, no
pidfile is created)
--timeZoneInfo arg full path to time zone info directory,
e.g. /usr/share/zoneinfo
--keyFile arg private key for cluster authentication
--noauth run without security
--transitionToAuth For rolling access control upgrade.
Attempt to authenticate over outgoing
connections and proceed regardless of
success. Accept incoming connections
with or without authentication.
--clusterAuthMode arg Authentication mode used for cluster
authentication. Alternatives are
(keyFile|sendKeyFile|sendX509|x509)
--nounixsocket disable listening on unix sockets
--unixSocketPrefix arg alternative directory for UNIX domain
sockets (defaults to /tmp)
--filePermissions arg permissions to set on UNIX domain
socket file - 0700 by default
--fork fork server process
--slowms arg (=100) value of slow for profile and console
log
--slowOpSampleRate arg (=1) fraction of slow ops to include in the
profile and console log
--networkMessageCompressors [=arg(=disabled)] (=snappy)
Comma-separated list of compressors to
use for network messages
--auth run with security
--clusterIpSourceWhitelist arg Network CIDR specification of permitted
origin for `__system` access.
--profile arg 0=off 1=slow, 2=all
--cpu periodically show cpu and iowait
utilization
--sysinfo print some diagnostic system
information
--noIndexBuildRetry don't retry any index builds that were
interrupted by shutdown
--noscripting disable scripting engine
--notablescan do not allow table scans
--shutdown kill a running server (for init
scripts)
Replication options:
--oplogSize arg size to use (in MB) for replication op
log. default is 5% of disk space (i.e.
large is good)
--master Master/slave replication no longer
supported
--slave Master/slave replication no longer
supported
Replica set options:
--replSet arg arg is <setname>[/<optionalseedhostlist
>]
--replIndexPrefetch arg specify index prefetching behavior (if
secondary) [none|_id_only|all]
--enableMajorityReadConcern [=arg(=1)] (=1)
enables majority readConcern
Sharding options:
--configsvr declare this is a config db of a
cluster; default port 27019; default
dir /data/configdb
--shardsvr declare this is a shard db of a
cluster; default port 27018
SSL options:
--sslOnNormalPorts use ssl on configured ports
--sslMode arg set the SSL operation mode
(disabled|allowSSL|preferSSL|requireSSL
)
--sslPEMKeyFile arg PEM file for ssl
--sslPEMKeyPassword arg PEM file password
--sslClusterFile arg Key file for internal SSL
authentication
--sslClusterPassword arg Internal authentication key file
password
--sslCAFile arg Certificate Authority file for SSL
--sslClusterCAFile arg CA used for verifying remotes during
outbound connections
--sslCRLFile arg Certificate Revocation List file for
SSL
--sslDisabledProtocols arg Comma separated list of TLS protocols
to disable [TLS1_0,TLS1_1,TLS1_2]
--sslWeakCertificateValidation allow client to connect without
presenting a certificate
--sslAllowConnectionsWithoutCertificates
allow client to connect without
presenting a certificate
--sslAllowInvalidHostnames Allow server certificates to provide
non-matching hostnames
--sslAllowInvalidCertificates allow connections to servers with
invalid certificates
--sslFIPSMode activate FIPS 140-2 mode at startup
Storage options:
--storageEngine arg what storage engine to use - defaults
to wiredTiger if no data files present
--dbpath arg directory for datafiles - defaults to
/data/db
--directoryperdb each database will be stored in a
separate directory
--noprealloc disable data file preallocation - will
often hurt performance
--nssize arg (=16) .ns file size (in MB) for new databases
--quota limits each database to a certain
number of files (8 default)
--quotaFiles arg number of files allowed per db, implies
--quota
--smallfiles use a smaller default file size
--syncdelay arg (=60) seconds between disk syncs (0=never,
but not recommended)
--upgrade upgrade db if needed
--repair run repair on all dbs
--repairpath arg root directory for repair files -
defaults to dbpath
--journal enable journaling
--nojournal disable journaling (journaling is on by
default for 64 bit)
--journalOptions arg journal diagnostic options
--journalCommitInterval arg how often to group/batch commit (ms)
WiredTiger options:
--wiredTigerCacheSizeGB arg maximum amount of memory to allocate
for cache; defaults to 1/2 of physical
RAM
--wiredTigerJournalCompressor arg (=snappy)
use a compressor for log records
[none|snappy|zlib]
--wiredTigerDirectoryForIndexes Put indexes and data in different
directories
--wiredTigerMaxCacheOverflowFileSizeGB arg (=0)
Maximum amount of disk space to use for
cache overflow; Defaults to 0
(unbounded)
--wiredTigerCollectionBlockCompressor arg (=snappy)
block compression algorithm for
collection data [none|snappy|zlib]
--wiredTigerIndexPrefixCompression arg (=1)
use prefix compression on row-store
leaf pages
Free Monitoring options:
--enableFreeMonitoring arg Enable Cloud Free Monitoring
(on|runtime|off)
--freeMonitoringTag arg Cloud Free Monitoring Tags
Configuration File
There are some differences between the parameters used in the configuration file and the command line. Mongodb currently [configuration file] https://docs.mongodb.com/v4.0/reference/configuration-options/#conf-file) ,
the configuration group mainly includes:
- systemLog Options
- processManagement Options
- cloud Options
- net Options
- security Options
- setParameter Option
- storage Options
- operationProfiling Options
- replication Options
- sharding Options
- auditLog Options
- snmp Options
The following is a typical configuration file:
processManagement:
fork: true
net:
bindIp: localhost
port: 27017
storage:
dbPath: /var/lib/mongo
systemLog:
destination: file
path: "/var/log/mongodb/mongod.log"
logAppend: true
storage:
journal:
enabled: true
Client
MongoDB Shell is MongoDB's a built-in interactive JavaScript shell enables you to access, configure and manage mongodb databases, users, etc.
Using this shell, you can perform a variety of tasks, from setting up user accounts to creating databases, and then querying the contents of databases.
# log in Mongo Shell without authenticating
mongo
# log in Mongo Shell witt authenticating
mongo admin --username root -p
MongoDB shell version v4.0.18
connecting to: mongodb://127.0.0.1:27017/?gssapiServiceName=mongodb
Implicit session: session { "id" : UUID("e808b886-30db-41dd-9464-40b52f041107") }
MongoDB server version: 4.0.18
> help
db.help() help on db methods
db.mycoll.help() help on collection methods
sh.help() sharding helpers
rs.help() replica set helpers
help admin administrative help
help connect connecting to a db help
help keys key shortcuts
help misc misc things to know
help mr mapreduce
show dbs show database names
show collections show collections in current database
show users show users in current database
show profile show most recent system.profile entries with time >= 1ms
show logs show the accessible logger names
show log [name] prints out the last segment of log in memory, 'global' is default
use <db_name> set current database
db.foo.find() list objects in collection foo
db.foo.find( { a : 1 } ) list objects in foo where a == 1
it result of the last line evaluated; use to further iterate
DBQuery.shellBatchSize = x set default number of items to display on shell
exit quit the mongo shell
Mongodb shell has two ways to interact with the database:
- Command line interactive operation
- Run the command script stored in the file (for example: shell_script.js)